ERP Definition
It is an enterprise integrated information system aimed at maximizing company-wide operational efficiency by comprehensively linking and
managing the organization’s core business processes and sharing information. The system is built by purchasing an ERP package developed
by a specialized vendor, selecting and customizing it according to the company’s needs, and partially modifying or supplementing it as necessary.
ERP Features
ERP generally possesses flexibility, comprehensiveness, openness, and integration. It also has the advantage of easily adapting
to changes in business processes and information technology during implementation and maintenance, such as user-driven development and the continuous
application of new information technologies.
Flexibility
- Can quickly respond to changes in business processes (various process alternatives can be implemented within the package)
Comprehensiveness
- Can support enterprise business functions centered on the accounting system
- Supports business regardless of industry or size
Openness
- Can interface with other systems and other companies (supports standardized interfaces)
Integration
- Provides enterprise-wide financial information through integrated information processing
- Drill down Analysis
Rapid Implementation
- Can respond quickly to business requirements through short-term implementation
Application of Best Practices
- Provides opportunities for BPR (Business Process Reengineering) through process design based on best practices
User-Driven Implementation
- Enhances efficiency in reflecting business requirements by allowing users to actively lead the project until system opening
Application of New Information Technologies
- Allows continuous application of new information technologies with upgrade periods of 6 months to 1 year
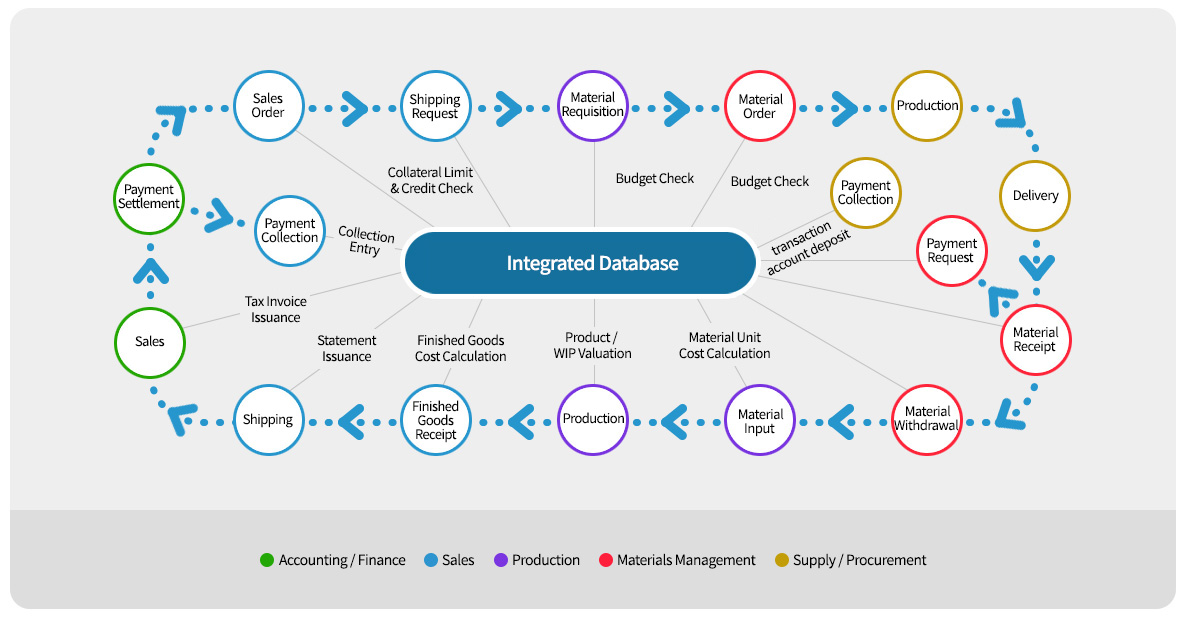
Solving Concerns About Corporate Business Processes and Information
ERP is a powerful tool that supports BPR, providing a foundation for simultaneously addressing concerns about advanced business processes
and the latest information infrastructure by continuously incorporating cutting-edge information technologies.
A Powerful Tool for BPR
- The advanced processes built into the package include the BPR concept, effectively allowing direct adoption of advanced management techniques.
- Applying the package automatically levels up business processes, driving innovation toward advanced operations.
- As an integrated solution covering order, production, and shipment processes, it enables organization-wide improvements and information integration rather than focusing on specific departments.
- Supports continuous future upgrades, allowing rapid adaptation to changes in the business environment.
Implementation of the Latest Information Technologies
- By receiving continuous functional upgrades driven by information technology development, the latest technologies can be quickly applied to business operations.
- Client/Server 3-Tier architecture
- Data Warehouse, Executive Information System
- Internet/Intranet
- Electronic Commerce
- Openness to all hardware and all OA (Office Automation) tools, etc.
Efficient Organizational Management
Through ERP adoption, organizations can improve efficiency by increasing productivity via enhanced customer service, rationalizing
decision-making through real-time data entry and updates, ensuring accurate information, and enabling organization-wide real-time communication across units.
Increased Productivity (Business Process)
- Improved customer service (shortened delivery times, enhanced quality)
- Faster processing for each function
- Increased sales capability
- Production at minimum cost through optimal production scheduling and automatic material ordering
Accuracy of Information (Information Technology)
- Provision of information for top management
- Accuracy of information ensured by real-time data entry and updates
- Rationalization of decision-making (utilizing accumulated data and accurate information at each level)
Efficient Organization
- Streamlined and customer-oriented organizational structure
- Utilization of advanced business processes
- Enables enterprise-wide communication across organizational units
Achieves low-cost, high-efficiency organizational management
An analysis of the effects on 1,480 companies worldwide that adopted ERP revealed the following findings.
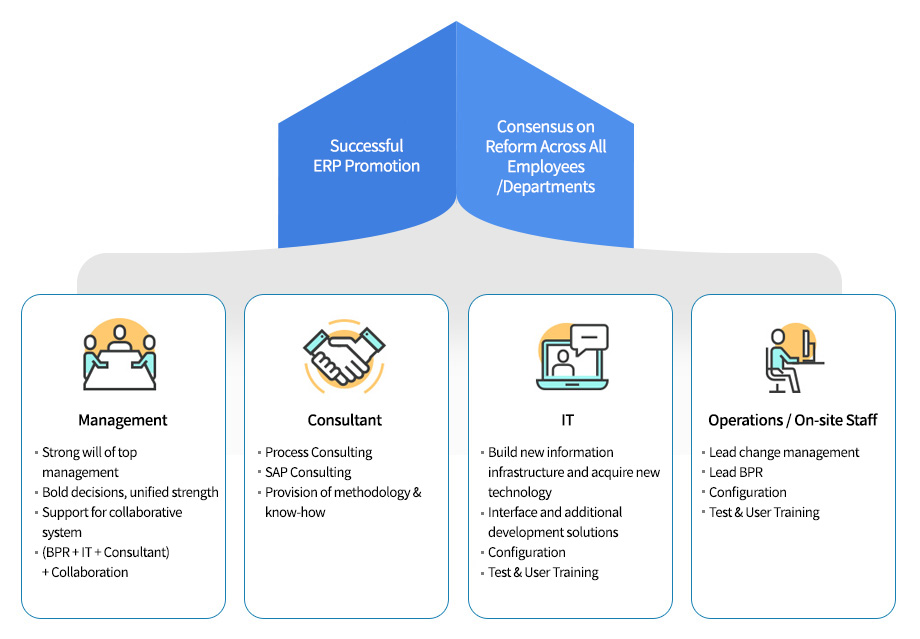
Key Success Factors for ERP Implementation
The ERP package is not just a passing trend, but an essential element for growth and development in the 21st century.
The success of ERP can only be guaranteed through an organized response centered on a task force (T/F) composed of PI, IT, consultants, and
operational staff, under the strong commitment and drive of management.
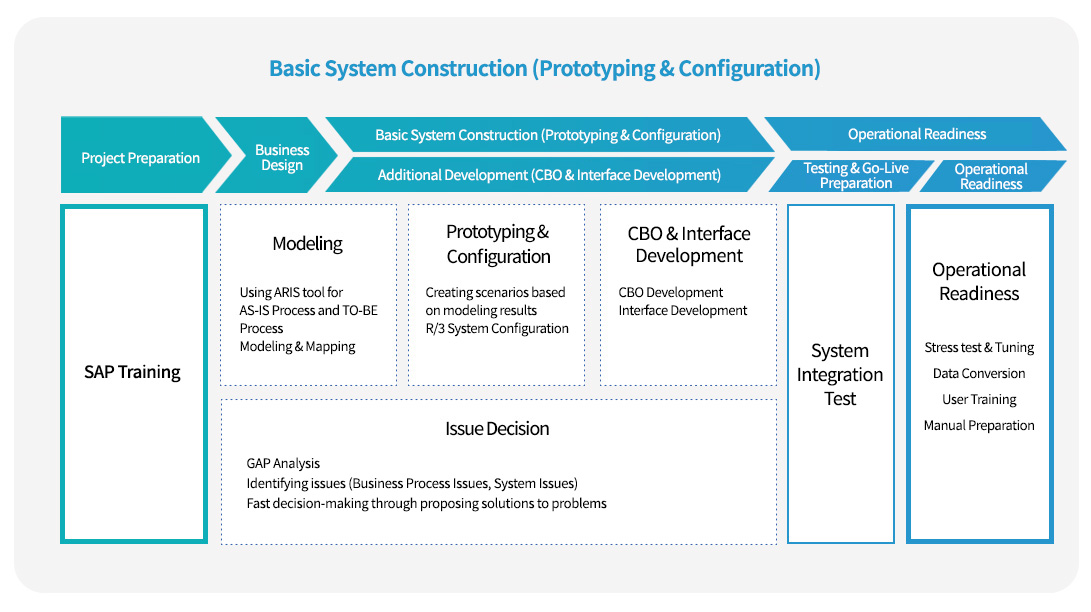
Implementation Methodology
The implementation of an ERP package proceeds through five stages: project preparation, business process design,
basic system construction, additional development, and operational readiness, and is carried out in a spiral (iterative) manner.